GitHub Actions Primer
Automate development tasks and deployment by using GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions provides free virtual machines (runners) that we can use to automate the repetitive tasks in our project repository. For example automating code testing, integration, building app and deployment on the server.
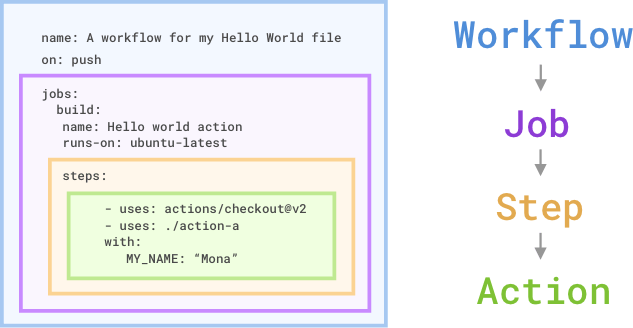
Workflow
We define a set of instructions for virtual machines. On every run the virtual machine follows this YAML file to execute the commands inside this text file.
Example: A pull request, issue or a commit in a repository triggers a workflow.
Jobs
Every workflow file contains one or more jobs. A set of instructions which are run on a separate virtual machine.
Example: A run tests, run build job described in a workflow.
Actions
The commands inside a job are called the actions.
Example: An action to SSH in to a server, execute Linux/Git commands or run/restart programs.
Source: microsoft.com
Example of a workflow
A workflow gets triggered automatically on every pull request merged into repository. Two jobs of code tests and deployment are run. These jobs run actions of run test, run build and deploy on the server.
Workflow YAML file
Located in the root in .github/workflows directory, workflow file is a simple yaml text file. Indentations are important. The jobs and action run in the order in which they are written in this file.
name: Spin up a runner
on: [push]
jobs:
spin-up-a-virtual-machine:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Execute command on server
run: ls -al
Workflow YAML File Explanation
name: Spin up a runner
on: [push]
Workflow starts with an optional name of the workflow.
The second line has a on: [push] directive to trigger the workflow. Every time someone pushes code to repository or a pull request is merged, this workflow gets triggered.
jobs:
spin-up-a-virtual-machine:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
jobs: groups all of the jobs in the workflow followed by the first job name spin-up-a-virtual-machine:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest directive creates a fresh virtual machine hosted by GitHub. A Linux server runner with latest version of Ubuntu in this case.
steps:
- name: Execute command on server
run: ls -al
The steps: groups together all the steps in spin-up-a-virtual-machine job.
Finally, when we have a runner with Ubuntu Linux, we execute the command ls -al in the run: directive.
Github repositories have Actions tab, this is where we can track the progress and output of this workflow.
Workflow Triggers
We use Git push trigger in our example, some other triggers are:
pull_request
release
issues
page_build
project_card
deployment
We can use GitHub actions API workflow_call to trigger a call to workflow or schedule a cron-job like timer schedule for workflow to run. Complete list of events that trigger a workflow is available here.
In the next few blog posts I will share CI/CD (continuous integration, continuous deployment) workflows. Example of some third-party open-source or GitHub Marketplace workflows.
